Welcome to my comprehensive guide to dental terms beginning with “H.” I’ll introduce you to a range of dental concepts, from halitosis to high-risk patients, providing essential information and guidance to maintain optimal oral health. Let’s dive into the world of dental knowledge, starting with the letter “H.”
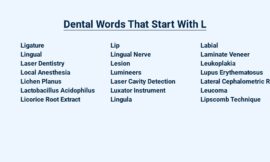
| Dental Words that Start with H | |
|---|---|
| Halitosis | Breath that has an unpleasant, foul odor. |
| Hard Tissue | A term used to describe teeth and the structures that support them, such as bone and cementum. |
| Hatched Restorations | A type of dental restoration that is made by etching a pattern into the tooth’s surface and then filling it with a composite resin. |
| Headgear | A type of orthodontic appliance that is worn on the head and is used to correct jaw problems. |
| Hemostasis | The process of stopping bleeding. |
| High-Speed Handpiece | A type of dental drill that is used to remove tooth decay and to prepare teeth for fillings and other restorations. |
| Hydrocolloid Impression Material | A type of impression material that is made from a gel-like substance. |
| Hygiene | The practice of keeping oneself clean and free of disease. |
Halitosis: Bad breath, caused by a variety of factors including poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and certain medical conditions.
Hard palate: The hard, bony tissue that forms the roof of the mouth.
Hard tissue: The hard tissues of the mouth include teeth, bone, and cementum.
Hawley retainer: A removable appliance used to keep teeth in their proper position after orthodontic treatment.
Hemisection: A surgical procedure in which a tooth is divided into two parts, one of which is removed.
Herpangina: A viral infection of the mouth and throat, causing sores and pain.
Herpetic gingivostomatitis: A viral infection of the gums and mouth, caused by the herpes simplex virus.
High-risk patient: A patient who is at increased risk of developing oral diseases, such as gum disease and tooth decay.
Horizontal overbite: A condition in which the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth excessively in a horizontal direction.
Hyperdontia: A condition in which there are extra teeth in the mouth.
Hyperplasia: An overgrowth of tissue, which can occur in the gums or other parts of the mouth.
Hypoplasia: An incomplete development of tissue, which can occur in the teeth or other parts of the mouth.
Hyposalivation: A condition in which the mouth produces less saliva than normal.
Hypersensitive teeth: Teeth that are sensitive to cold, heat, or sweets.
Hygiene: The practice of keeping the mouth clean and healthy, including brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups.
Dental Words That Start With H
Halitosis
Halitosis, commonly known as bad breath, is an unpleasant odor emanating from a person’s mouth. It can be caused by various factors, including poor dental hygiene, certain foods, medical conditions, and smoking.
Halitosis can be embarrassing and may affect social interactions.
Healthy Gums
Healthy gums are essential for maintaining good oral health.
They provide a strong foundation for teeth, protect against infection, and help prevent gum disease.
Maintaining healthy gums involves brushing and flossing regularly, eating a balanced diet, avoiding smoking, and visiting the dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
Hard Tissue
Hard Tissue: Calcified tissues in the body, including bones and teeth.
In dentistry, hard tissue refers specifically to the enamel, dentin, and cementum of the tooth.
Hard Palate
Hard Palate: The hard, bony portion of the roof of the mouth, forming the anterior part of the palate. It is covered by a thick layer of mucous membrane.
Hawley Retainer
Hawley Retainer: A removable orthodontic appliance often used to retain teeth in their corrected positions after braces. It is made of a metal wire framework with an acrylic or plastic base that fits over the teeth.
Hemisection
Hemisection is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the root and half of a tooth, usually a molar. This is done when decay or infection has damaged one root beyond repair.
The remaining healthy portion of the tooth can then be restored with a filling, crown, or bridge.
Herpangina
Herpangina, a common childhood illness, is caused by a virus.
Symptoms include fever, sore throat, and painful mouth ulcers.
Treatment involves rest, pain relievers, and fluids.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
Herpetic gingivostomatitis, commonly known as herpangina, is a contagious viral infection that affects the mouth and throat.
It is caused by the herpes simplex virus and typically occurs in young children.
Symptoms include painful sores in the mouth, fever, and difficulty swallowing.
Treatment involves pain relievers and supportive care.
High-Risk Patient
High-Risk Patient: Individuals with underlying medical conditions or compromised immune systems, requiring special precautions and considerations during dental treatment to minimize potential complications.
Horizontal Overbite
Horizontal Overbite: A condition where the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth excessively in a horizontal plane, causing an abnormal bite.
This misalignment can lead to discomfort, difficulty chewing, and potential dental problems.
How to Brush Your Teeth Properly
- Rinse your toothbrush with water and apply a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste.
- Brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the fronts, backs, and tops.
- Brush gently with small, circular motions.
- Brush for at least two minutes, twice a day.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles are worn.
How to Floss Your Teeth Properly
- Break off about 18 inches of floss and wrap it around your middle fingers, leaving a few inches in between.
- Hold the floss taut with your thumb and forefinger, and gently slide it between two teeth.
- Move the floss up and down, and side to side, to remove plaque and food particles.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each tooth, and be sure to floss behind your back molars.
How to Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and replace it every 3-4 months.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks, which can damage your teeth.
- Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice daily and flossing once a day. Avoid sugary foods and drinks, as they can feed plaque bacteria.
Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help detect and treat gum disease early.
Quit smoking, as it can increase your risk of gum disease.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay
- Brush teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks.
- Visit the dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
- Consider fluoride treatments or sealants for extra protection.
Final Verdict
The realm of dentistry encompasses a myriad of terms beginning with the letter “H.” From halitosis, the unpleasant odor emanating from the mouth, to Hawley retainers, orthodontic appliances used to correct misaligned teeth, these terms encapsulate the wide spectrum of oral health. Understanding these concepts empowers individuals to maintain optimal oral hygiene, preventing gum disease, tooth decay, and other dental ailments.
Regular checkups with a dental professional remain paramount in ensuring a healthy and radiant smile.