Welcome to my comprehensive guide to dental words beginning with the letter ‘A’. Join me as I explore an array of terms, from abscesses and amalgam to anesthesia and aphthous ulcers.
Learn about appliances, apicoectomies, arch wires, attrition, alveolar ridges, and alveoli.
Together, let’s demystify the world of dentistry, one word at a time.
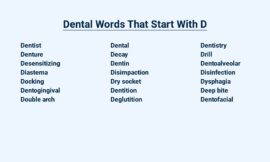
| Dental Words Starting with A | ||
| Abscess | Amalgam | Anesthesia |
| Apicoectomy | Articulator | Attrition |
| Bacteria | Biopsy | Bleaching |
| Bonding | Bridge | Bruxism |
| Calculus | Canker Sore | Caries |
| Cavity | Cement | Cleaning |
| Crown | Curettage | Cyst |
| Dentin | Dentist | Dentures |
| Diagnosis | Diastema | Drill |
| Enamel | Endodontics | Extraction |
Abrasion: The gradual wearing away of tooth structure due to mechanical forces, such as improper brushing or grinding.
Abscess: A localized collection of pus in the gums or jaws, caused by bacterial infection.
Abutment: A tooth or implant used to support a bridge or other dental restoration.
Acrylic resin: A synthetic material used in the construction of dentures, crowns, and other dental appliances.
Alginate: A material used to make dental impressions.
Alloy: A mixture of two or more metals, used in the construction of dental restorations and appliances.
Amalgam: A mixture of mercury and other metals, used to fill cavities in teeth.
Anesthesia: A medication used to numb the pain of dental procedures.
Anticaries agent: A substance that helps to prevent tooth decay.
Antimicrobial: A substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi.
Apicoectomy: The surgical removal of the root tip of a tooth.
Appliance: A dental device used to correct or improve the function of the teeth or jaws.
Arch wire: A metal wire used to align teeth in braces.
Articulator: A device used to simulate the movements of the jaw, allowing dentists to create restorations that fit properly.
Atraumatic restorative treatment (ART): A method of restoring teeth that uses hand instruments and no anesthesia.
Attrition: The gradual wearing away of tooth structure due to normal use, such as chewing.
Autoclave: A device used to sterilize dental instruments and equipment.
Avascular necrosis: A condition in which bone tissue dies due to lack of blood flow.
Avulsion: The complete displacement of a tooth from its socket.
Azithromycin: An antibiotic used to treat dental infections.
Acid etch technique: A method of preparing tooth surfaces for bonding.
Adhesive dentistry: The use of bonding agents to repair or restore teeth.
Air abrasion: A method of removing decay from teeth using a stream of air and abrasive particles.
Alveolar bone grafting: A procedure used to build up the bone in the jaw to support dental implants.
Alveolar ridge: The bony ridge that forms the border of the upper and lower jaws.
Alveoloplasty: A surgical procedure to reshape the alveolar ridge.
Amalgam separator: A device used to remove amalgam particles from wastewater.
Ameloblast: A cell that forms the enamel of the teeth.
Amelogenesis imperfecta: A genetic disorder that affects the development of the enamel of the teeth.
Analgesic: A medication used to relieve pain.
Angina: A condition characterized by chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart.
Angulated abutment: An abutment that is angled to allow for the placement of a dental restoration in a difficult-to-reach area.
Angulation: The angle at which a dental instrument or restoration is positioned.
Antibiotic: A medication used to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Anti-inflammatory drug: A medication used to reduce inflammation.
Antiseptic: A substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms on living tissue.
Apex: The tip of the root of a tooth.
Apexification: A procedure to create an artificial apex on a tooth with an open root canal.
Apical foramen: The opening at the tip of the root of a tooth through which the nerve and blood vessels enter and exit.
Apical granuloma: A small, inflammatory mass at the apex of a tooth.
Apical periodontitis: Inflammation of the tissues surrounding the apex of a tooth.
Articulating paper: A thin, carbon-coated paper used to check the occlusion of the teeth.
Artificial tooth: A tooth-shaped restoration that is used to replace a missing tooth.
Asbestos: A fibrous mineral that was once used in the construction of dental materials, but is now known to be a health hazard.
Aspirator: A device used to remove saliva and other debris from the mouth during dental procedures.
Astringent: A substance that causes the contraction of tissues.
Attachment: The connection between a tooth and the surrounding tissues.
Attrition: The gradual wearing away of tooth structure due to normal wear and tear.
Autoclave: A device used to sterilize dental instruments and equipment.
Auxiliary: A person who assists a dentist in providing dental care.
Dental Words Starting With A
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that forms in the body due to infection. In dentistry, an abscess can occur in the mouth, usually around the root of a tooth or in the gums.
It can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort.
Treatment typically involves draining the abscess and addressing the underlying infection.
Amalgam
Amalgam, a commonly used dental material, is an alloy of mercury with other metals like silver, tin, and copper. Mixed with mercury to form a soft, moldable compound, it is primarily used to fill cavities, restore damaged teeth, and create strong, durable dental restorations.
Anesthesia
Anesthesia: A state of controlled, temporary unconsciousness induced by medication, allowing medical procedures to be performed without pain. Local anesthesia numbs a specific area, while general anesthesia affects the entire body.
Aphthous ulcer
Aphthous ulcers, also known as canker sores, are small, painful sores that can develop in the mouth.
They are usually round or oval and can be white, yellow, or gray.
Aphthous ulcers can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, certain foods, and hormonal changes.
Appliance
Appliance refers to any device or apparatus used in dentistry to correct, maintain, or improve the function, position, or appearance of teeth. Examples include braces, retainers, and mouthguards.
Appliances can be removable or fixed, and they are customized to meet the individual needs of each patient.
Apicoectomy
Apicoectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove the infected root tip of a tooth. This procedure is usually done when the infection cannot be treated with antibiotics or root canal therapy.
Apicoectomy can help to relieve pain and prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the mouth.
Arch wire
An arch wire is a component of orthodontic braces used to align and straighten teeth. It is a thin, flexible wire that is attached to brackets bonded to the teeth.
The arch wire gradually moves the teeth into the desired positions over time.
Attrition
Attrition is the gradual wearing away of tooth structure due to mechanical forces such as grinding or clenching of teeth. This can result in loss of tooth structure, sensitivity, and pain.
Treatment options may include bite guards, dental restorations, or orthodontic treatment.
Alveolar ridge
Alveolar ridge, a bony ridge in the upper and lower jaws, supports and anchors the teeth.
It forms the socket walls for each tooth and provides stability during chewing and biting.
Alveolus
Alveolus, the tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged, play a vital role in respiration. These delicate structures, lined with capillaries, facilitate the efficient transfer of gases, ensuring the body’s oxygen supply and removal of waste carbon dioxide.
Final Verdict
This dental lexicon focused on terms commencing with the letter “A,” providing a comprehensive overview of essential concepts in dentistry.
From abscesses and amalgam to anesthesia and aphthous ulcers, we explored the diverse vocabulary used in dental care.
Furthermore, we delved into specialized terminology such as appliances, apicoectomy, arch wires, and attrition, highlighting their significance in dental procedures and oral health maintenance.
Understanding these terms empowers individuals to engage effectively with dental professionals, fostering better communication and informed decision-making regarding their oral health journey.